LeetCode in TypeScript
133. Clone Graph
Medium
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node { public int val; public List
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
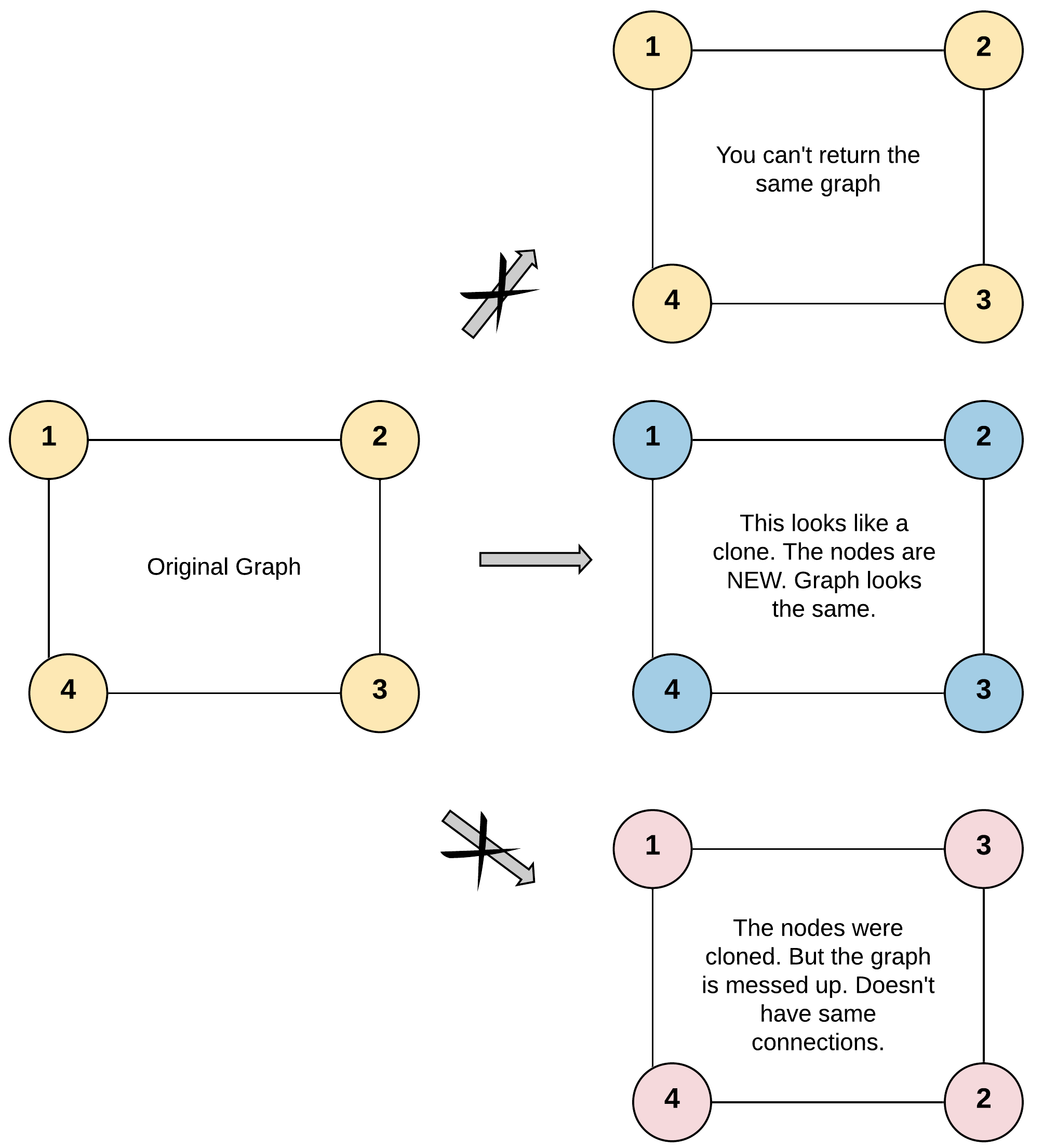
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation:
There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
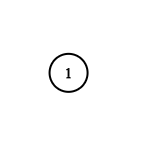
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = []
Output: []
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
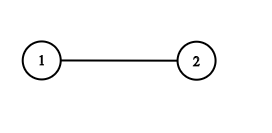
Input: adjList = [[2],[1]]
Output: [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Solution
class Node {
val: number
neighbors: Node[]
constructor(val: number = 0, neighbors: Node[] = []) {
this.val = val
this.neighbors = neighbors
}
toString(): string {
const result: string[] = []
for (const node of this.neighbors) {
if (node.neighbors.length === 0) {
result.push(node.val.toString())
} else {
const result2: string[] = []
for (const nodeItem of node.neighbors) {
result2.push(nodeItem.val.toString())
}
result.push(`[${result2.join(',')}]`)
}
}
return `[${result.join(',')}]`
}
}
function cloneGraph(node: Node | null): Node | null {
const processedNodes = new Map<Node, Node>()
return cloneGraphHelper(node, processedNodes)
}
function cloneGraphHelper(node: Node | null, processedNodes: Map<Node, Node>): Node | null {
if (node === null) {
return null
}
if (processedNodes.has(node)) {
return processedNodes.get(node)!
}
const newNode = new Node(node.val)
processedNodes.set(node, newNode)
for (const neighbor of node.neighbors) {
const clonedNeighbor = cloneGraphHelper(neighbor, processedNodes)
if (clonedNeighbor !== null) {
newNode.neighbors.push(clonedNeighbor)
}
}
return newNode
}
export { Node, cloneGraph }

